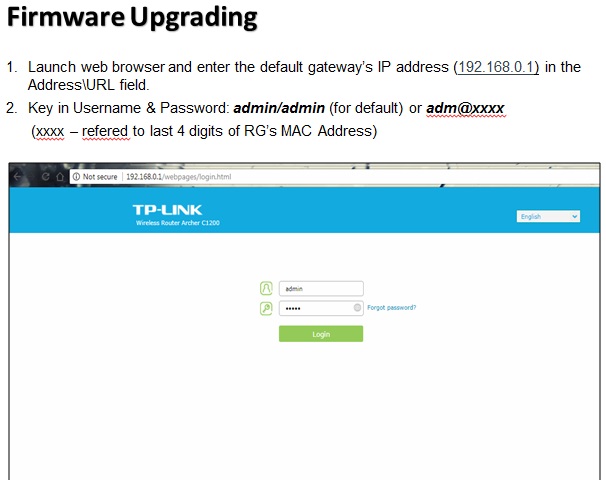
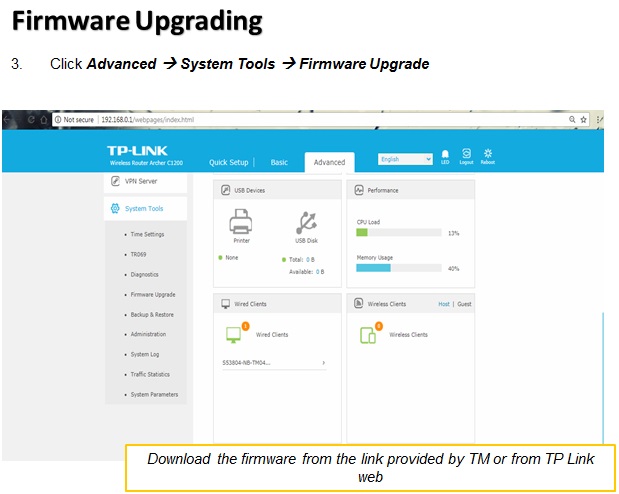
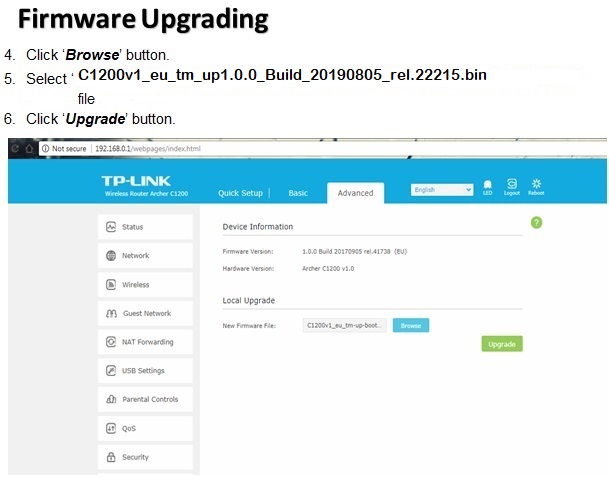
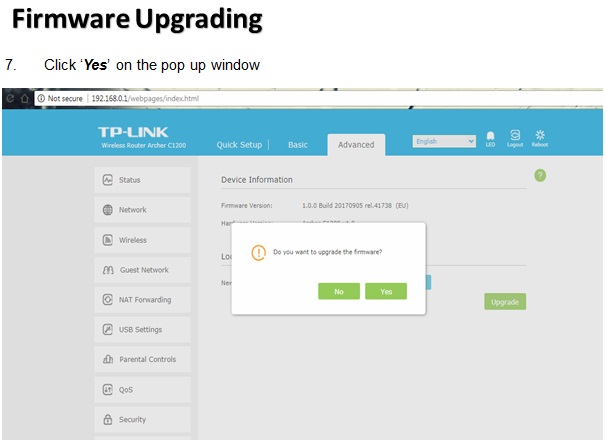
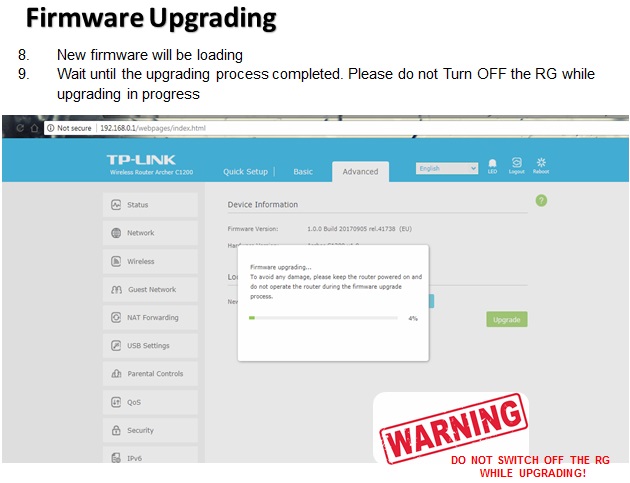
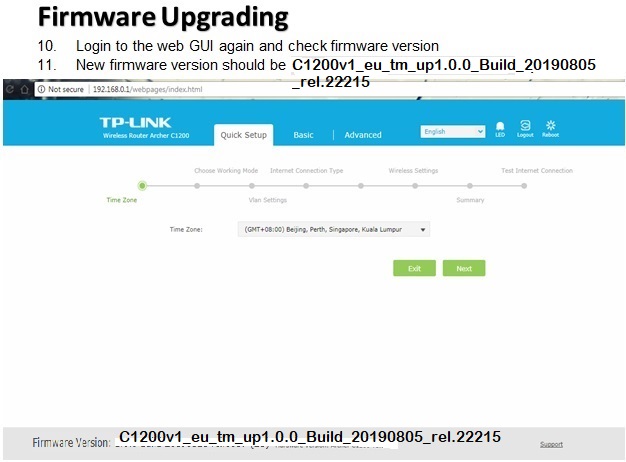
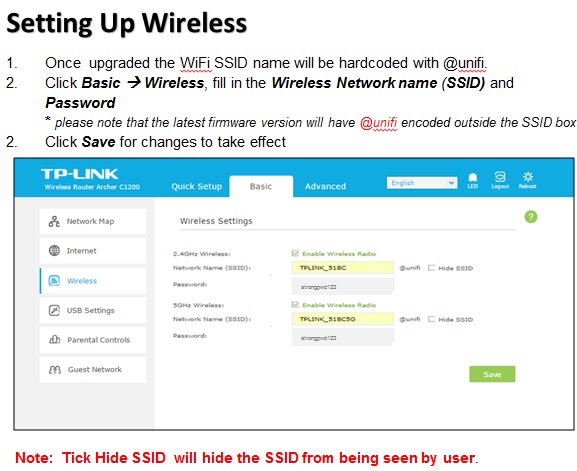
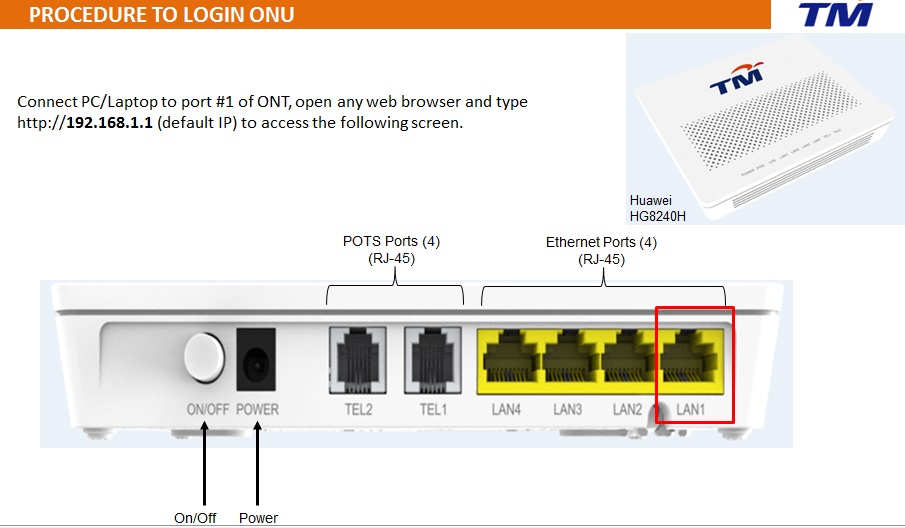
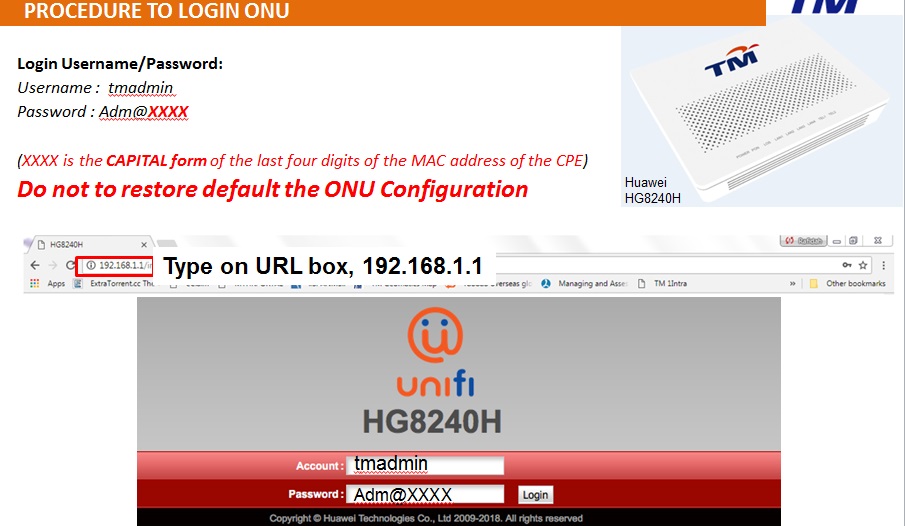
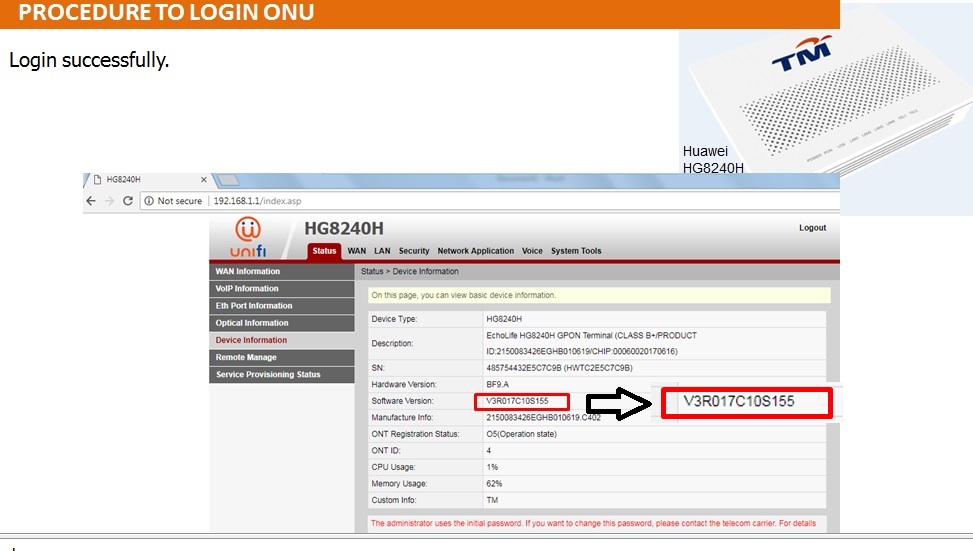
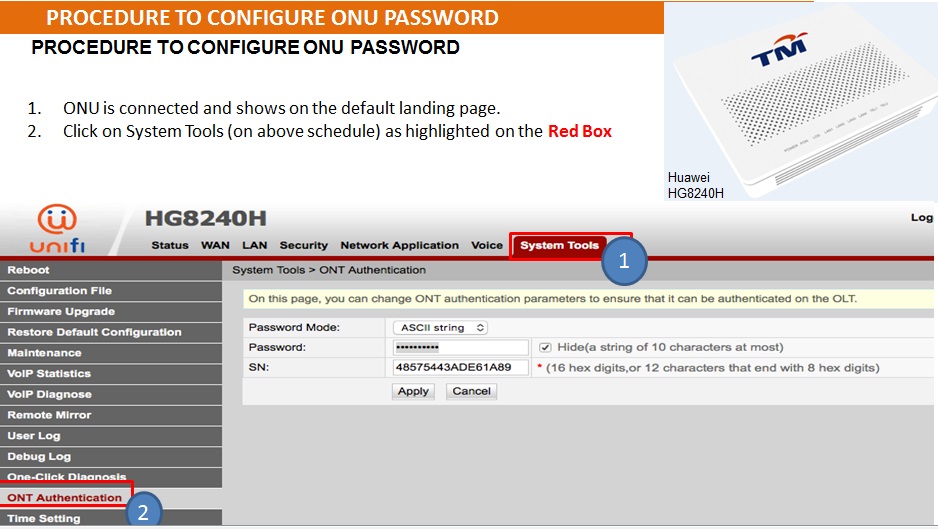
There are many wireless standards in use today, and newer technologies can bond multiple channels/frequencies together to achieve higher
throughput.
First, keep in mind that in data communications, speed is measured in kilo
bits (or mega
bits) per second, designated as kbps, or Mbps. You can check our
bits/bytes conversion calculator for reference.
Below is a breakdown of the various
802.11 WiFi standards and their corresponding maximum speeds. Theoretical wireless speeds (combined
upstream and
downstream) are as follows:
802.11b – 11 Mbps (2.4GHz)
802.11a – 54 Mbps (5 GHz)
802.11g – 54 Mbps (2.4GHz)
802.11n – 600 Mbps (2.4GHz and 5 GHz) – 150Mbps typical for network adapters, 300Mbps, 450Mbps, and 600Mbps speeds when bonding channels with some routers
802.11ac – 1300+Mbps (5 GHz) – newer standard that uses wider channels, QAM and spatial streams for higher throughput
Actual wireless speeds vary significantly from the above theoretical maximum speeds due to:
distance – distance from the
access point, as well as any physical obstructions, such as walls, signal-blocking or reflecting materials affect signal propagation and reduce speed
interference – other wireless networks and devices in the same frequency in the same area affect performance
shared bandwidth – available
bandwidth is shared between all users on the same wireless network.
In addition, net IP layer
throughput of WiFi is typically 60% of the air link rate due to WiFi being half-
duplex with ACKs, and being CSMA/CA. The number of simultaneous connections, and even the type of wireless security can affect and slow down some older routers with inadequate processors/memory.
Below is a breakdown of actual real-life average speeds you can expect from wireless routers within a reasonable distance, with low interference and small number of simultaneous clients:
802.11b – 2-3 Mbps downstream, up to 5-6 Mbps with some vendor-specific extensions.
802.11g – ~20 Mbps downstream
802.11n – 40-50 Mbps typical, varying greatly depending on configuration, whether it is mixed or N-only network, the number of bonded channels, etc. Specifying a channel, and using 40MHz channels can help achieve 70-80Mbps with some newer routers. Up to 100 Mbps achievable with more expensive commercial equipment with 8×8 arrays, gigabit ports, etc.
802.11ac – 70-100+ Mbps typical, higher speeds (200+ Mbps) possible over short distances without many obstacles, with newer generation 802.11ac routers, and client adapters capable of multiple streams.

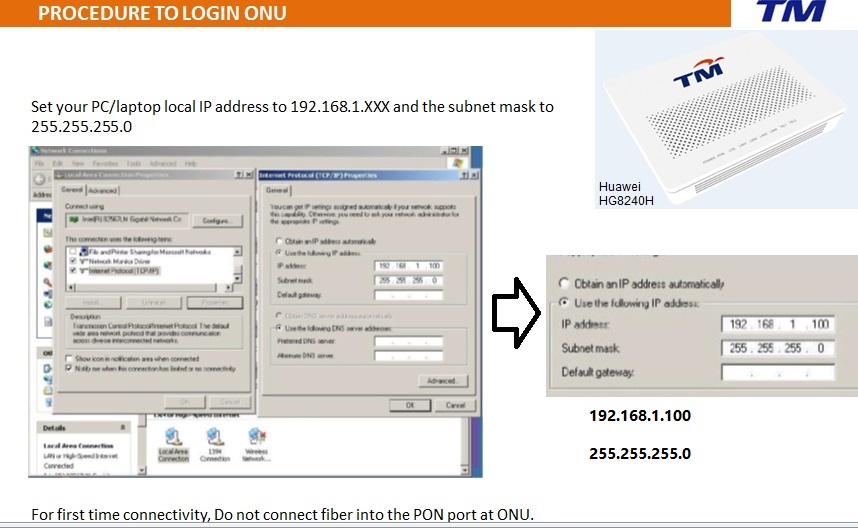



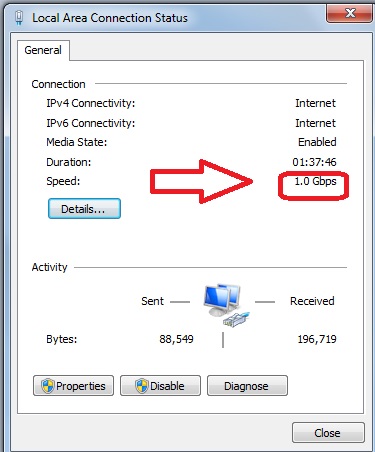
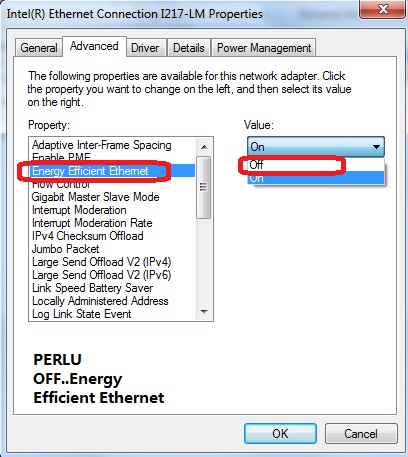
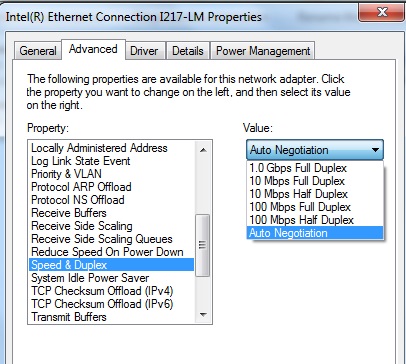
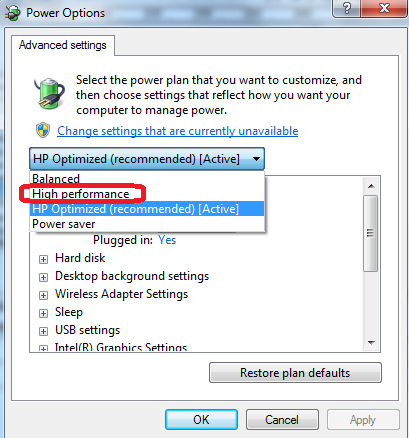
 atau Safari utk run speedtest.
atau Safari utk run speedtest.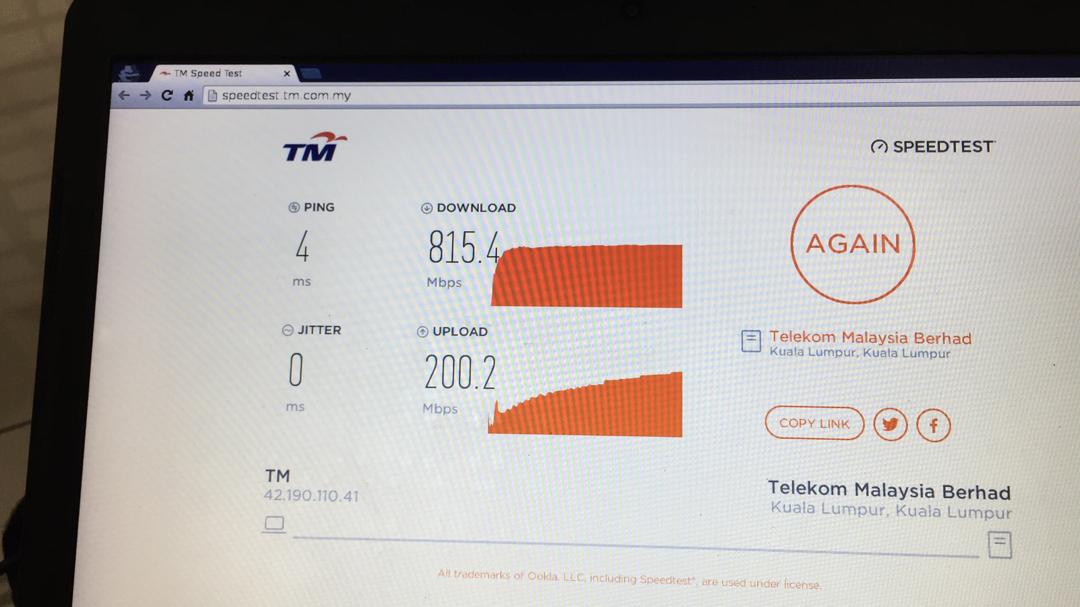
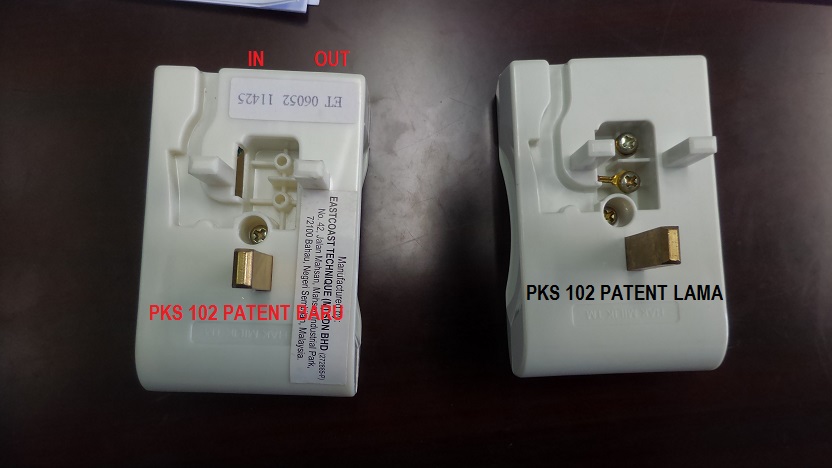
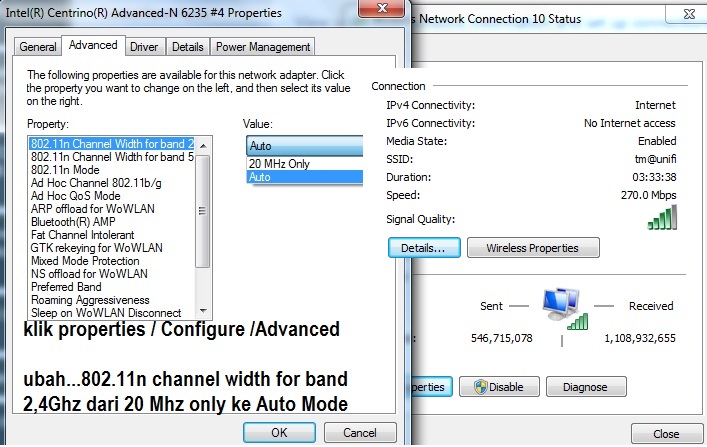


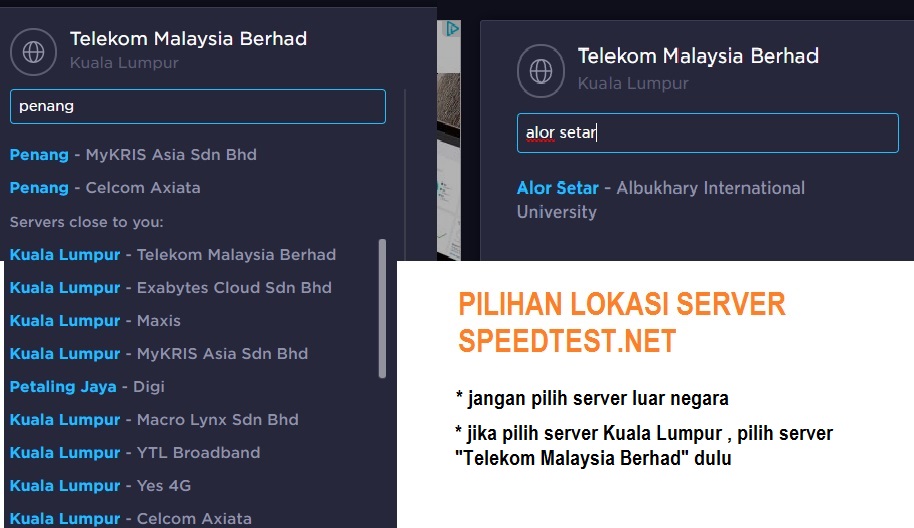

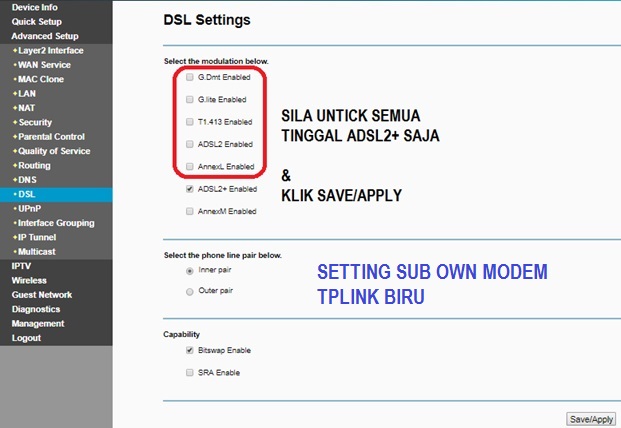 so far bacaan line quality OK GUNA MODEM TM
so far bacaan line quality OK GUNA MODEM TM